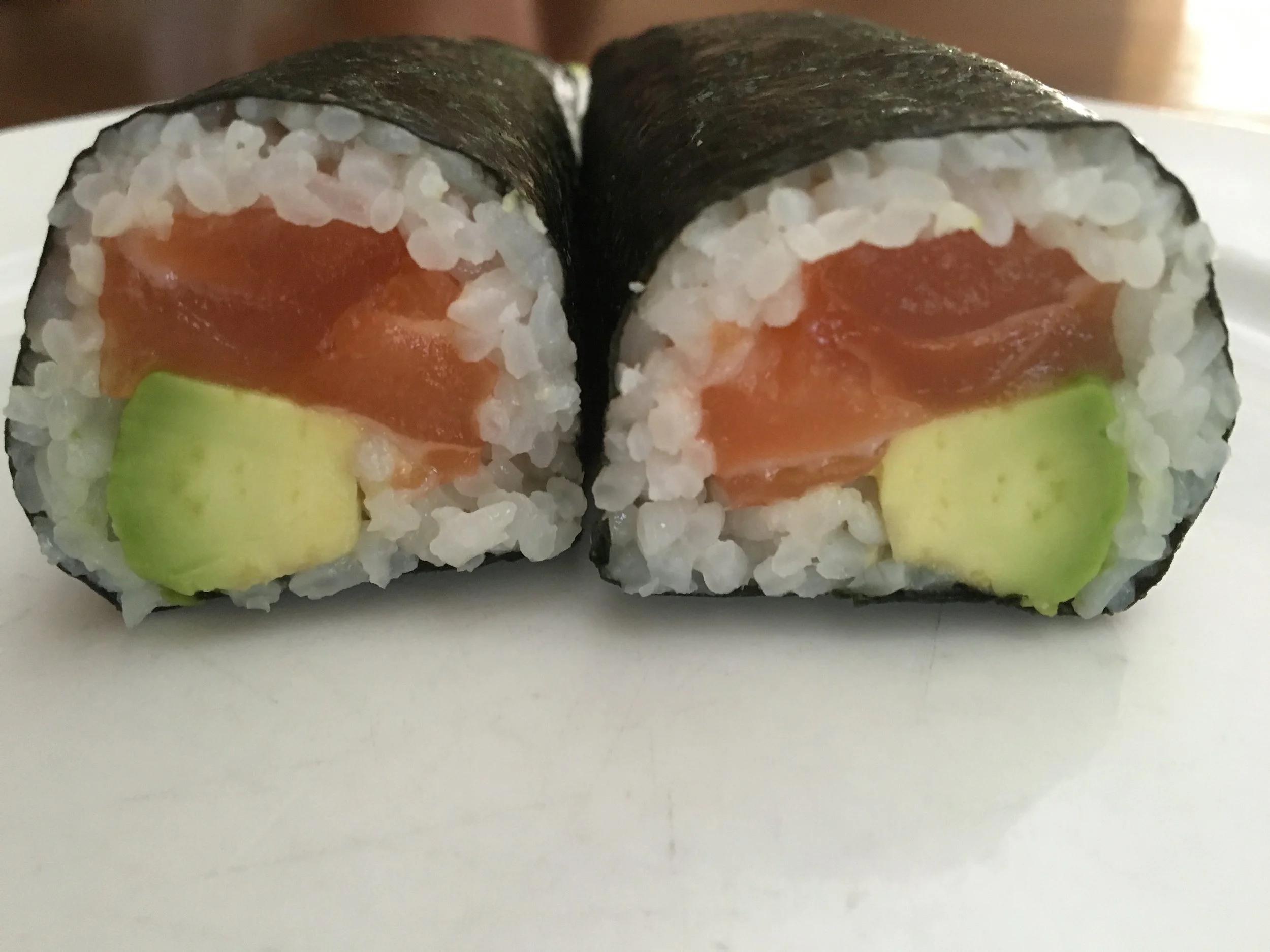
The first time I ever ate a sushi roll was in Sydney - tuna and avocado as I was a bit wary of anything raw at that stage! It would have been over 15 years ago and I remember how excited I was about this ‘new’ take-away option that was nowhere to be found in Melbourne back then!
Sushi rolls and rice-paper rolls are easy to buy and easy to eat for a quick lunch or snack on the run. Sushi rolls are a combination of rice, seaweed and protein/veg filling while rice-paper rolls are based on rice noodles, vegetables, herbs and protein.
Although they are a similar shape, size and cost, sushi and rice paper rolls can be different nutritionally:
Carbohydrate
It’s all about rice for both sushi and rice paper rolls, great news for those who follow a gluten-free style of eating.
Sushi rolls – Although white rice is often high glycemic index (GI), the combination of the rice with vinegar and protein/fat in the filling help to reduce the GI. However, sushi rolls pack A LOT of rice into each little roll. Choose brown rice when it’s on offer – not lower GI but boosts fibre and nutrient content.
Rice paper rolls – Rice noodles are lower GI and the amount of carbohydrate is usually a lot lower than sushi rolls. Rice paper rolls are also available in a lower-carb varieties, with more vegetables packed in, increasing the fibre and nutrients and reducing carbohydrate.
Protein
Both types of rolls commonly contain fish, chicken, tofu, duck or beef for protein. Rice paper rolls often fit in a bit more protein serve, but it depends where you get them and exactly how they are made.
Fat
Both varieties of rolls are generally quite low in fat, but fillings like avocado and fish will provide some healthy fats. A salmon sushi roll doesn’t take the place of having a fish fillet meal however . If the filling is crumbed and deep fried, or combined with mayonnaise, this will bump up the fat also.
Kilojoules
Sushi rolls range from 150-200 calories each, depending on filling and size, while rice paper rolls are general a lot lower and often under 100 calories per roll. This is without sauces – which can be high in sugar and salt, so keep sauce to a small serve.
So which is best?
Overall nutrition
Please remember that both sushi and rice paper rolls are decent take-away food options! But if we are comparing, rice paper rolls most likely take the prize for the most nutritious, especially those packed with fresh vegetables, herbs and fish. HOWEVER – brown rice sushi, with the iodine-rich seaweed, brings sushi up a couple of rungs on the nutrition ladder.
Energy levels
Rice paper rolls may be lower GI but they contain a lot less carbohydrate, so although they may theoretically help blood glucose levels, they may not keep you going for quite as long as sushi handrolls.
Exercise performance
Sushi rolls contain more carbohydrate so may keep you going for longer as a pre-exercise lunch or snack. Rice paper rolls can contain more vegetables and herbs however, which are important for day-to-day health and performance, but not so much a fuel source.
For more pre-exercise snack ideas, go to High performance snacks you should be eating at 3.30pm to get the best out of your post-work workout.
Weight management
Rice paper rolls are a clear winner with significantly less kilojoules, especially if packed with more vegies vs noodles. Sushi rolls are still a great option however, and will likely fill you up for longer if you need to keep going for a busy afternoon ahead. For more weight management tips 5 secrets of the French - how to eat the foods you like and not get fat.
In perspective
Both sushi and rice paper rolls are delicious and nutritious options to enjoy as a quick take-away choice….there are slight differences in carbohydrate and nutrients but either are going to be better than many other high-fat, high-sugar take-aways.
I would love to send your free performance nutrition updates, recipes and news about my new book I am working on about super food for performance, please add your details on my Thoughts page.