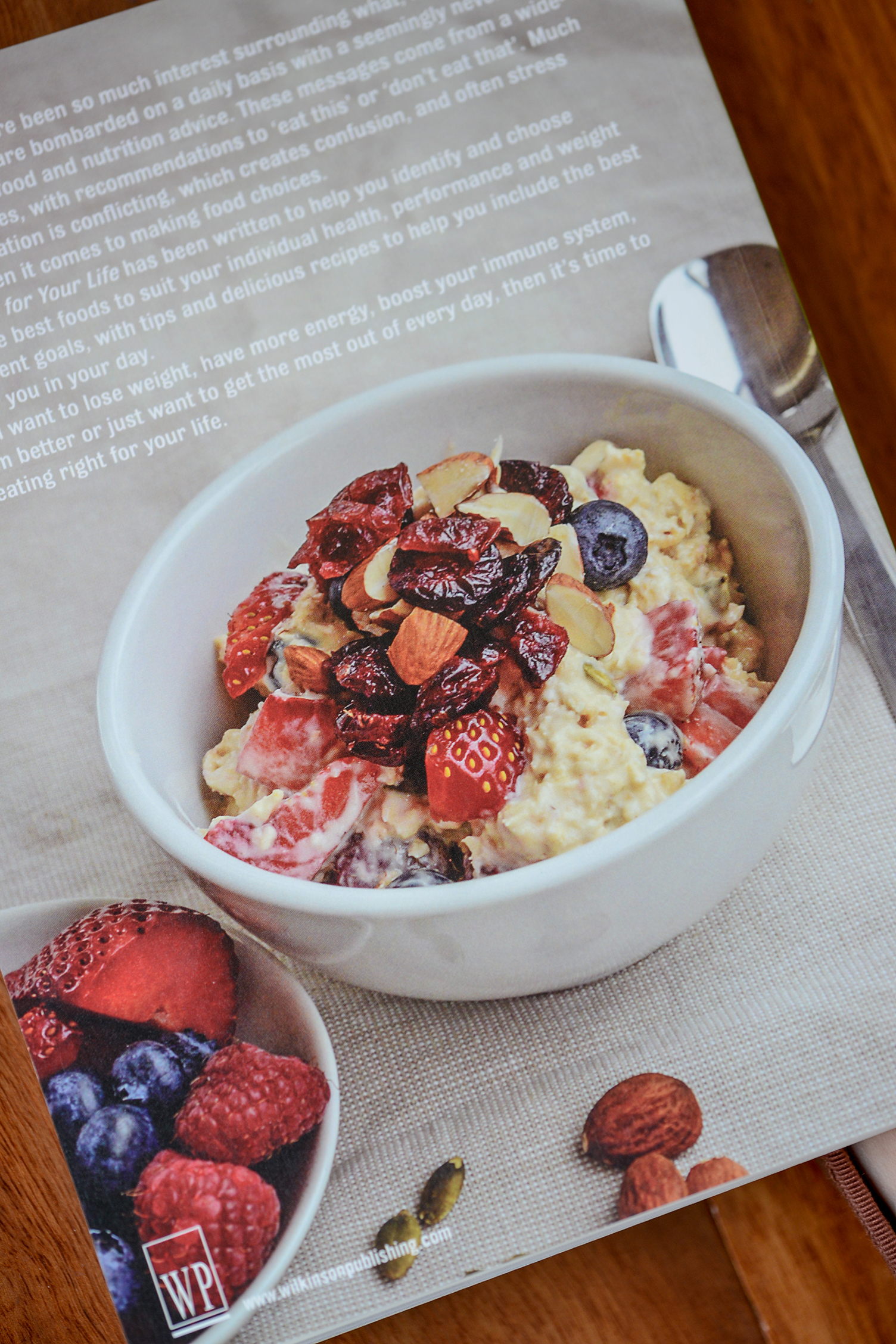
Back cover of my new bookazine, photo courtesy of Bec Doyle Photography
With my new book 'Eat Right For Your Life' being released earlier this week, I thought it was timely to share with you a snippet of what it's all about. If you love going to the gym and enjoying the health and fitness benefits that regular exercise provides, then this postis particularly relevant for you. Not that the book is all about sports nutrition - it covers a range of lifestyle stages, but of course I had to include reference to nutrition for active people.
It's amazing how much time and effort goes into producing a small book, from research, to writing content to developing recipes, to photography. It was a pleasure to work with my good friend and talented photographer on the images (a busy weekend at my place last September cooking, styling and snapping). The book looks at different life stages and lifestyles and provides nutrition tips and a list of some of the 'best' and 'beware' foods for each, followed by recipes based on the needs of each particular group.
I thought I would share part of the introduction and the ten 'best' foods from the 'Gym Junkie' chapter, which focuses on nutrition for individuals who go to the gym regularly with the goal of building fitness, strength and improved body composition (I dont' love the word 'junkie' but it does get the idea across as to who that chapter may appeal to):
.....'In order to help build muscle you need adequate protein. This doesn’t necessarily mean spending your weekly pay packet on fancy supplements, but you will definitely need to eat protein-rich foods regularly, and extra kilojoules to support muscle gains.
Protein is made up of individual amino acids, and it is likely that you will be able to achieve adequate amino acid intake from a carefully planned and timed dietary intake. Protein supplements may be useful in a number of situations and they are formulated to meet the specific amino acid needs of training. Perhaps the main benefit of supplements is the convenience factor, considering most high-quality protein sources require an esky to transport.
Sure, protein is important, but you also need to make sure you have some nutritious, low-GI carbohydrates to keep you energised, as well as including some healthy fats. Vitamins and minerals are critical for energy levels and recovery from training, so don’t neglect your daily fruit, vegetables, nuts, seeds and wholegrains.
10 best foods
Milk
It’s in everybody’s fridge, but few of us realise the amazing potential of milk. Milk is a naturally high biological value protein supplement, containing all of the essential amino acids the muscles need to repair and grow. One 300ml glass of milk contains about 10g of high quality protein. In a smoothie, milkshake or just on its own, milk is great for pre- and post-exercise or as an extra source of protein, carbohydrates, vitamins and minerals. Milk also contains more electrolytes than many sports drinks, making it a terrific option as a rehydrating fluid.
Turkey
Chicken has long been a favourite food for body builders because of its high protein content but it is not the only poultry option to help build muscle. Remove the skin and turkey is a super-lean way to meet your amino acid needs. Versatile and quick to cook, turkey makes the perfect sandwich filler or post-gym meal.
Greek yoghurt
If you are serious about your health and fitness, yoghurt will be a staple on your weekly shopping list. Sure, yoghurt is rich in protein and is a convenient pre- or post-gym snack, but it will also help to keep your insides healthy. Yoghurt contains ‘good’ bacteria, important for optimal digestive health. Aim for at least 1 cup of good quality yoghurt every day. Natural or Greek yoghurt is lower in sugar and additives than fruit yoghurts, and make sure you read the label because some Greek yoghurts are higher in protein.
Bok choy
If you are working on your muscles, the focus is often on protein rather than the importance of variety for optimising fitness and performance. Green vegetables are a perfect example, rather than just cooking up chicken and rice, add in some Asian greens such as bok choy, pak choy, wom bok (Chinese cabbage), choy sum (Chinese silverbeet) and gai lan (Chinese broccoli). These delicious vegetables are brimming with nutrients including calcium, iron and folate. Why not try including one new green vegetable every week. (To find out whether kale is king, visit my previous Thoughts article Green Leaf Goodness: Kale vs Spinach vs Rocket, and the winner is.....)
Oats
Low in fat, high in fibre and low glycemic index, a delicious bowl of porridge will keep you going all morning, the perfect start to a busy day. Make with milk and add some extra yoghurt or chopped nuts/seeds for extra protein. If you are not a porridge fan, oats are just as nutritious in natural muesli or made into homemade Bircher muesli (such as the one pictured at the start of this post, recipe featured in 'Eat Right For Your Life').
Eggs
Eggs have fallen in and out of favour over the years, but current research shows that eggs can be enjoyed regularly, even if you do have high cholesterol. For an active person, eggs are one of the highest biological value proteins you will find. The egg white is practically pure protein, but don’t neglect the yolk! Egg yolks are rich in minerals and important fat-soluble vitamins, which are often lacking in active people who keep to a low-fat way of eating. If your cholesterol is on the edge you may need to be careful beyond six yolks per week, although you may be able to enjoy more. Eggs are a tasty and nutritious option if you are active.
Rice milk
You may not have tried rice milk, but it is one of the best fluids to mix with your protein powder after the gym. Why? The carbohydrate in rice milk has a high glycemic index, which can aid in in recovery and promote absorption of the amino acids from protein powder post-exercise. Rice milk does not contain much protein itself, but mixed with a protein supplement it provides an effective stimulant for muscle synthesis.
Herbs (including garlic and chilli)
If you are serious about improving your health, you should be eating herbs. Herbs add flavour to foods and contain negligible kilojoules when used in a mixed dish, but pack a concentrated nutrient punch.
Many fresh herbs have been found to contain vitamin, mineral and antioxidant concentrations many times that of standard vegetables, and using a range of herbs will provide a variety of health (and taste!) benefits. Common herbs that you can be grown at home include basil (great in salads and with tomato based sauces), parsley (use with omelettes and fish), coriander (terrific in Asian style dishes, especially with chicken and seafood), rosemary (lean lamb and potatoes) and mint (both sweet and savoury dishes).
Kangaroo
One of the leanest meats around, and packed with iron and zinc, kangaroo will help you meet your protein needs and keep you energised. It is also an economical option if you are watching your budget. If you haven’t tried it, have a go but be careful not to overcook or the meat will become tough (marinate prior if possible). Beef is a great choice too for quality protein and minerals.
Oranges
It is widely accepted that oranges and other citrus fruits are good for our immune system due to their Vitamin C content (one orange contains double the recommended daily intake). But this isn’t the only benefit of eating oranges. Oranges contain antioxidants (including vitamin C) that can help the body recover from exercise. Vitamin C also helps the body to absorb iron. If that’s not convincing enough, oranges are often recommended for people with rheumatoid arthritis due to their anti-inflammatory effect. The anti-inflammatory potential of oranges may be due to flavonoid antioxidants, vitamin C itself or something else entirely, but this effect may potentially play a role in reducing the risk of a range of chronic diseases that are related to inflammation.
You can learn more about the best and beware foods for different life stages and lifestyles in 'Eat Right For Your Life', available now at bookstores, newsagents and various online retailers.
P.S. If you are a keen gym-goer, it may be useful to consult with an accredited sports dietitian to discuss your food and supplement requirements in more detail, and work with an exercise physiologist or appropriately qualified personal trainer to develop a training program for best results.